Misoprostol: women's autonomy in the tapestry of healthcare
Misoprostol is a synthetic prostaglandin medication used to prevent and treat stomach and duodenal ulcers, induce labor, cause an abortion, and treat postpartum bleeding due to poor contraction of the uterus.
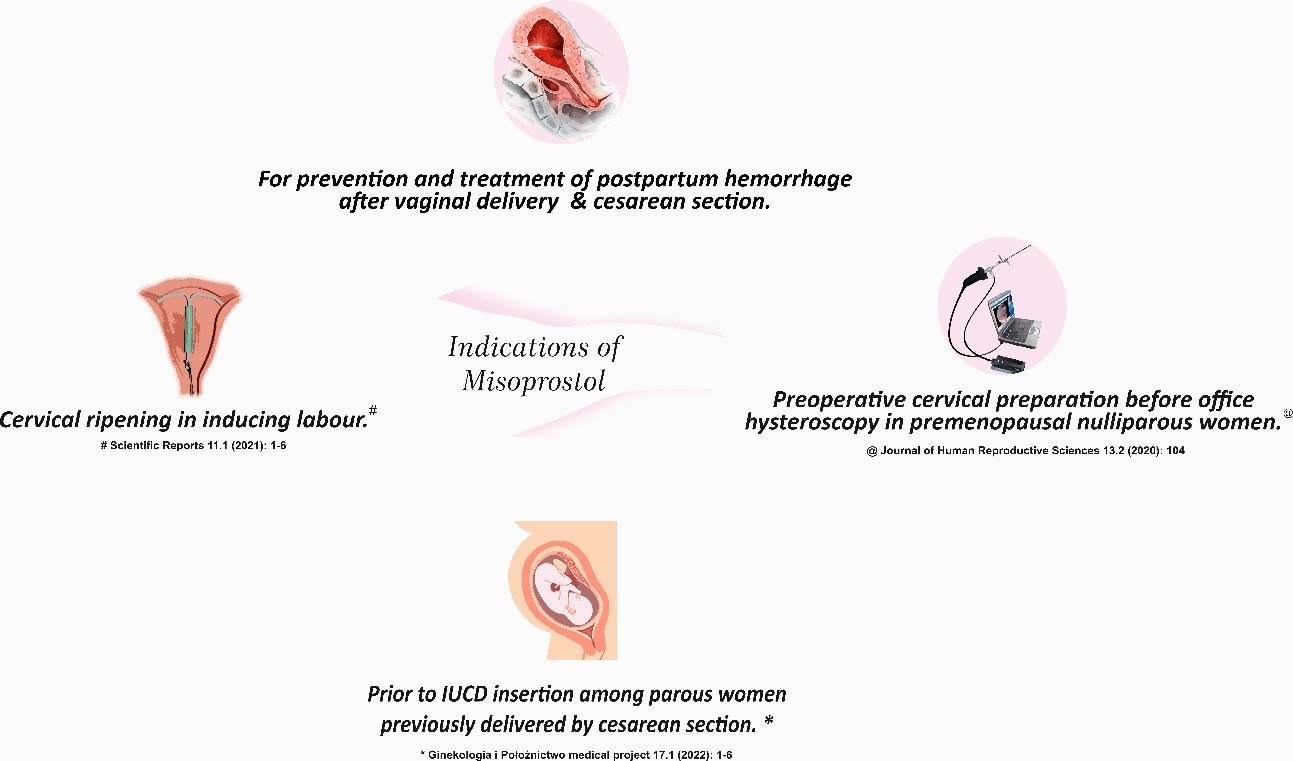
Misoprostol is commonly used in gynaecology for various purposes (fig. 1), including:
- Medical Abortion: Misoprostol is used in combination with another medication called mifepristone for medical abortion. It helps induce contractions of the uterus, leading to the termination of an early pregnancy. Medical abortion with misoprostol is generally considered safe and effective when conducted under proper medical supervision.
- Cervical Ripening: Misoprostol can be used to prepare the cervix for procedures such as dilation and curettage (D&C) or hysteroscopy. It helps soften and dilate the cervix, making these procedures easier and less uncomfortable.
- Labor Induction: In cases where labor needs to be induced, misoprostol may be used to promote uterine contractions and initiate labor. It can be an option when medical intervention is necessary for the well-being of the mother or baby.
- Management of Postpartum Hemorrhage: Misoprostol can be used to prevent and treat postpartum hemorrhage (excessive bleeding after childbirth). It helps contract the uterus and reduce the risk of excessive bleeding.
- Treatment of Missed Miscarriage: In some cases of missed miscarriage (when the embryo has stopped developing but the body has not expelled it), misoprostol can be used to help the body expel the non-viable pregnancy tissue.
- Induction of Fetal Demise: In cases where a pregnancy is non-viable and poses a risk to the mother’s health, misoprostol may be used to induce fetal demise before a medical procedure or induction of labor.
- Management of Menstrual Disorders: Misoprostol can also be used to treat certain menstrual disorders, such as heavy menstrual bleeding or irregular periods.
Misoprostol, like any medication, can have adverse effects. Some common adverse effects associated with the use of misoprostol include:
- Uterine Contractions and Bleeding: Misoprostol’s primary effect is to stimulate uterine contractions, which can lead to vaginal bleeding. This is expected during certain medical procedures like abortion or labor induction, but excessive bleeding can be a concern and should be monitored.
- Abdominal Pain: Uterine contractions caused by misoprostol can result in abdominal cramping and discomfort.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting as a side effect of misoprostol.
- Diarrhea: Misoprostol can lead to diarrhea in some cases due to its effects on the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Headache: Headaches are a possible side effect of misoprostol.
- Fever and Chills: Fever and chills can occur as a response to the uterine contractions induced by misoprostol.
- Dizziness or Light-headedness: Some people may feel dizzy or lightheaded after taking misoprostol.
- Allergic Reactions: While rare, allergic reactions to misoprostol are possible and could manifest as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
It’s important to note that the severity and occurrence of these adverse effects can vary from person to person. Additionally, misoprostol may have different effects depending on its specific use (e.g., medical abortion, cervical ripening, labor induction).
Misoprostol should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on its appropriate use, potential risks, and monitoring for adverse effects. If you experience any unexpected or severe adverse effects while using misoprostol, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
Misoprostol’s mechanism of action is primarily related to its effect on the smooth muscles of the uterus and the gastrointestinal tract. It is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) analog and exerts its effects through interaction with specific receptors in these tissues:
It’s important to note that misoprostol should only be used under medical supervision due to its potential side effects, contraindications, and interactions with other medications. Its use should be guided by a healthcare provider who can tailor the treatment to the specific medical condition and needs of the patient.
It’s important to emphasize that misoprostol should only be used under the guidance and supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. The dosage and administration of misoprostol can vary depending on the specific medical situation, and its use should be tailored to individual patient needs. Additionally, misoprostol can have side effects and potential complications, so its use should be well-informed and monitored by a healthcare provider.
